What Is an MX Record and How to Check It for Better Sender Reputation
Table of Contents
Every campaign begins with one question: Will it reach the inbox? Even the most captivating content can fail if a domain’s mail servers aren’t configured correctly. MX records, the DNS entries that direct where email should be delivered, play a silent but crucial role in this process. Misconfigured MX records can cause bounces, lower deliverability, and gradually erode your sender reputation. This guide walks you through how MX records work, how to check them, and how verification tools help ensure your emails land where they belong.
What Is an MX Record?
An MX (Mail Exchanger) record is a type of DNS record that tells the internet which mail server is responsible for receiving email for a domain. It doesn’t store emails itself; instead, it provides the hostname of the receiver’s mail server that should handle incoming messages.
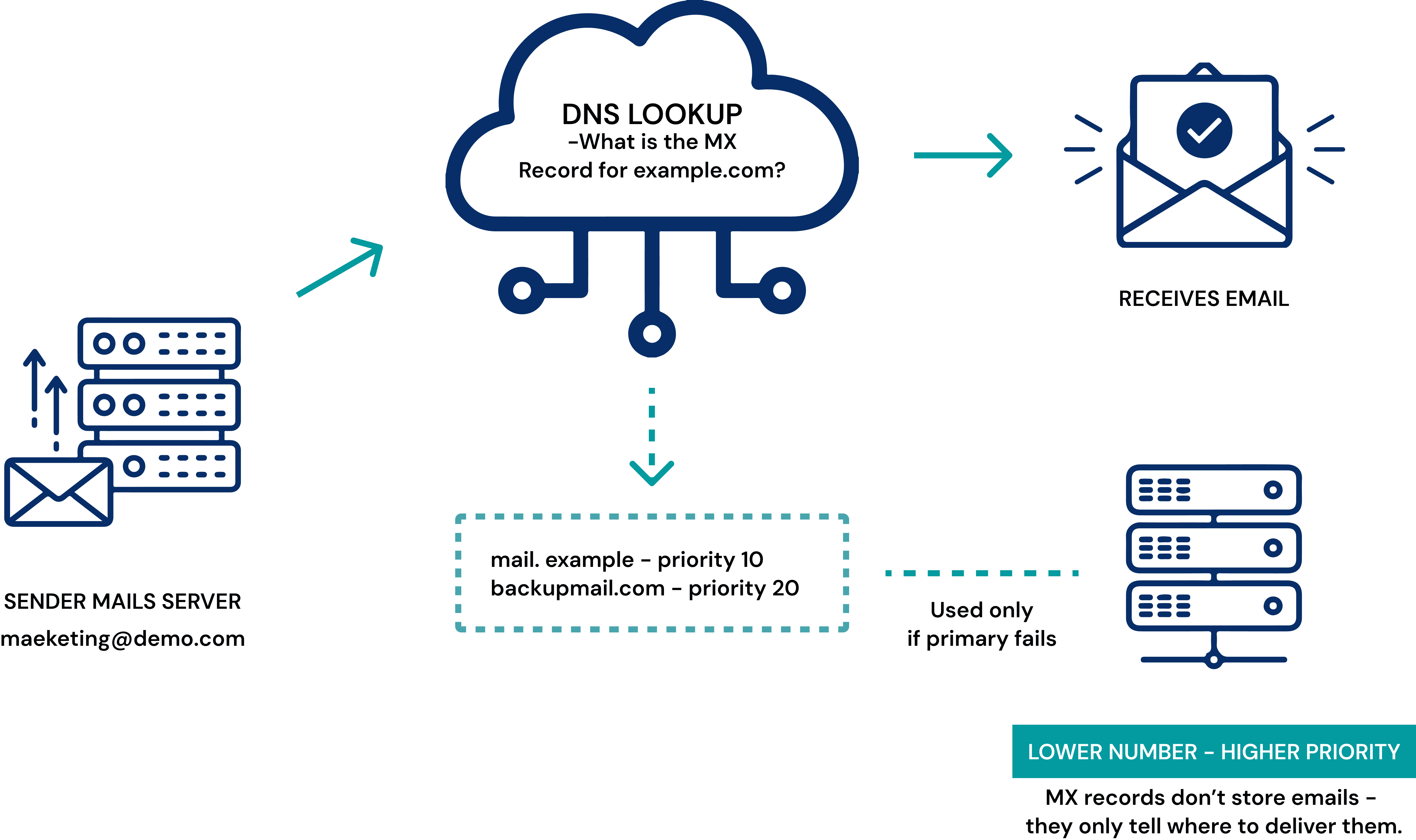
When someone sends an email, the sender’s mail server looks up the recipient domain’s MX record in DNS. It (the sender’s mail server) reads the hostname of the receiver’s mail server (e.g., mail.example.com) and then connects to that server to deliver the message. MX records also include a priority value, which determines the order in which multiple receiver mail servers are used. A lower number indicates a higher priority.
Example:
Suppose you send an email from support@demo.com to user@example.com.
✔️
Your sender mail server (for demo.com) looks up the MX record for example.com.
✔️
The MX record points to mail.example.com with priority 10.
✔️
The sender mail server connects to the receiver mail server (mail.example.com) and delivers the email.
✔️
If a backup receiver mail server exists with priority 20, it will only be used if the primary server is unavailable.
Without a valid MX record, the sender mail server cannot locate the receiver mail server, and the email will not be delivered.
How an MX Record Delivers Email
How to Check MX Records
Before diagnosing deliverability issues, confirm that a domain’s MX records are set correctly. Here are the most reliable ways to check them:
Using Online MX Lookup Tools
Online MX lookup portals are the quickest way to verify whether a domain’s email infrastructure is configured correctly. By entering a domain name, these tools instantly display:
●
MX hostnames
●
MX priorities
●
Mail hosting provider
●
Status of DNS responses
These tools are especially valuable for marketers, business owners, and IT administrators, as they provide a clear view of how email for a domain is routed and whether its DNS configuration supports proper mail delivery.
You should use online MX lookup tools when configuring new email hosting, diagnosing bounce or routing failures, validating DNS changes, onboarding client domains, or confirming domain readiness before sending outbound campaigns. They help identify missing, incorrect, or non-responsive MX records issues that directly impact whether a domain can successfully receive mail.
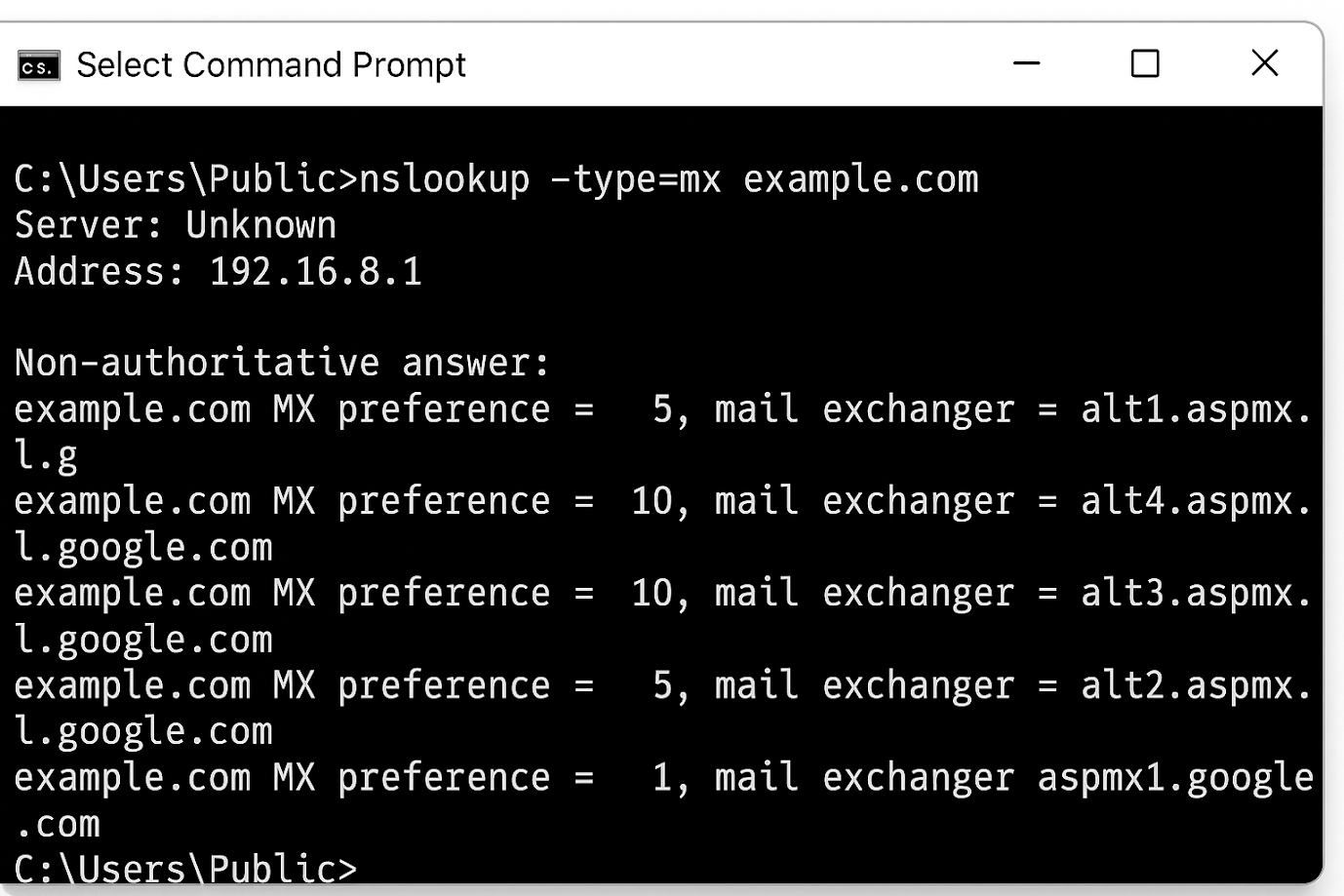
Using Command Line Tools
For users who prefer direct DNS queries, command-line tools provide highly accurate results from authoritative DNS servers. These tools eliminate the interface layer of online portals, making them ideal for technical users who need precise, real-time DNS information.
Windows
nslookup -type=mx yourdomain.com
macOS / Linux
dig mx yourdomain.com
On macOS and Linux, the command dig mx yourdomain.com returns the MX hostnames, MX priorities, and the DNS server that responded. Command-line lookups are useful for validating DNS propagation, comparing results across resolvers, and confirming that a domain’s mail routing is correctly configured.
Automated MX Record Validation Within Email Verification Platforms
Many advanced email verification tools automatically validate MX records as part of their standard email validation process. When an email address is checked, these services perform real-time DNS queries to verify the domain’s MX configuration.
This integrated MX validation allows you to:
●
Confirm that the domain’s mail servers are properly configured and accepting mail.
●
Detect domains with missing, expired, or misconfigured MX records that could cause delivery failures.
●
Identify high-risk or non-existent domains to reduce bounce rates and improve deliverability.
By incorporating MX checks directly into email validation, these platforms eliminate the need for separate DNS lookups, providing comprehensive insights into domain health and mail routing reliability in one streamlined step. This enhances email list hygiene and helps ensure successful message delivery.
Common MX Record Issues and Their Implications
Below are the most frequent MX record issues and how they impact email deliverability:
Missing MX Records
If a domain has no MX records configured, it cannot receive email. Any message sent to the domain will be returned with a bounce. DNS lookups will show no MX entries, signaling an immediate delivery failure.
MX Records Point to Invalid or Non-Responsive Servers
Even if MX records exist, the mail servers they point to may be offline, unreachable, or misconfigured. This results in intermittent delivery failures. DNS lookups may show correct hostnames, but SMTP connectivity tests (e.g., via telnet) will fail, indicating a non-functional mail server.
Priority Misconfigurations
MX records include priority values that determine the order in which mail servers are used. Incorrect priorities can cause emails to route through backup or inactive servers first, leading to delays or bounce messages. Reviewing priority values using DNS tools helps identify misrouted traffic.
MX Hostnames Not Linked to Active SMTP Servers
Some domains list MX hostnames that do not correspond to operational SMTP servers. Attempts to deliver email to such hosts result in errors like “SMTP unavailable” or “host unreachable”. Verifying MX hostnames against active SMTP services is critical for identifying this issue.
Temporary DNS Outages or Propagation Delays
Short-term DNS failures or delays in propagation can make MX records unreachable for hours. This affects large-scale email campaigns and can generate sporadic delivery failures. Monitoring MX records over time can help identify these transient issues.
How MX Records Impact Email Deliverability
Mailbox providers such as Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo rely on MX records to verify a domain's legitimacy and routing reliability. When MX records are missing or misconfigured, these providers may treat the domain as unreliable, which can directly affect email deliverability.
Effects of MX Record Issues on Email Delivery
●
Increased Hard Bounces: Emails sent to domains with broken MX records fail immediately, harming your sender reputation and overall deliverability.
●
Triggering Spam Filters: Domains with unstable or misconfigured MX records are more likely to be flagged by spam filters.
●
Lower Inbox Placement: Even messages to valid recipients may be routed to the Spam or Promotions folder.
●
Accumulation of Reputation Damage: Repeated delivery failures or MX timeouts degrade the domain’s trust score, affecting future campaigns.
●
Potential Rejection by Providers: Misconfigured Domain MX records may cause email providers to block incoming and outgoing messages.
Best Practices for Managing MX Records
Healthy MX records are essential for maintaining reliable email delivery and preserving sender reputation. The following best practices ensure your domain’s mail routing remains stable and trustworthy.
●
Maintain Accurate and Reachable MX Records
Ensure your domain always has valid MX records pointing to working mail servers. If you change email providers, update these records right away and test them to keep your mail flowing without interruption.
●
Use Reliable, Dedicated Mail Servers
Choose reliable, well-known mail servers rather than low-quality or shared hosting. A strong MX setup helps your email stay up and running and builds trust with mailbox providers.
●
Monitor MX Record Health Continuously
DNS or server problems can happen without warning. If your domain’s MX records break or go offline, the sender’s mail server won’t be able to find your mail server. This causes emails sent to you to bounce, so regular MX monitoring helps you catch problems early.
●
Configure MX Priorities Correctly
Set your main mail server to the lowest priority, and give your backup servers higher values. This way, incoming mail will follow the right delivery path.
●
Validate Email Lists Before Sending
Before you start an email campaign, use email verification tools to find domains with broken or inactive MX records. Catching these issues early helps you avoid unnecessary bounces and protect your sender reputation.
How ExactVerify Performs MX Checks
When an email address is submitted for validation, ExactVerify runs a structured, multi-layered verification workflow that evaluates the domain’s DNS and MX records, as well as mailbox availability. This ensures that only deliverable, no-risk email addresses are approved.
Real-Time DNS Lookup
This begins by querying the domain’s authoritative DNS servers to retrieve its MX records. This step confirms the:
●
Domain existence
●
DNS is responsive
●
MX records are present
For example, in the sample email address support@yourdomain.com, you retrieved the MX hostname aspmx.l.google.com, confirming proper DNS configuration.
MX Record Validation
Each MX record is evaluated to verify that it is:
●
Valid: Which is correctly formatted and points to a real mail exchanger
●
Resolvable: The hostname resolves to an IP address
●
Routed correctly: Priorities are logical and compliant
●
Linked to an operational mail server: The MX corresponds to an active provider (e.g., Google Workspace)
This ensures the domain’s email routing infrastructure is functional.
Deliverability Decision
Finally, it combines the results of all previous checks and assigns a deliverability status such as:
●
Valid
●
Invalid
●
Undeliverable
●
Risky
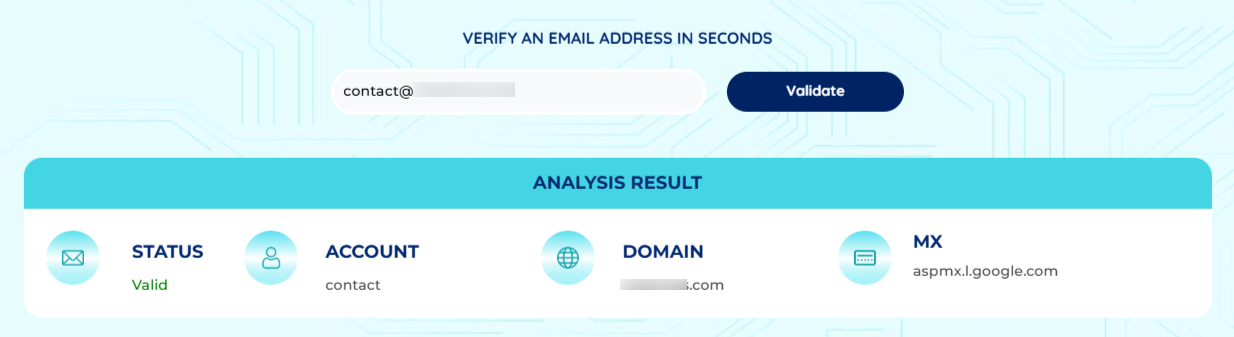
In this image, the above mentioned email passed all checks, including MX lookup and SMTP simulation, resulting in a valid classification.
This automated workflow ensures you do not send messages to domains with broken MX records or inactive mail servers, protecting your sender reputation and improving overall deliverability. For more information about email deliverability issues, read our blog on Email Deliverability vs Email Delivery
Bottom Line
MX records are essential for reliable email delivery. To protect your reputation, always validate MX records before sending emails, ideally using an email validation or MX lookup tool. This reduces bounces, improves deliverability, and helps maintain a strong sender reputation.
Validating MX records is vital when sending emails to protect your reputation, reduce delivery issues, and ensure consistent email delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on MX Records
1. Can wrong MX records hurt the sender reputation?
Yes. If the domain MX records are incorrect or missing, emails sent to the domain may fail because senders’ mail servers cannot locate the mail server. This can trigger misconfiguration warnings, and when combined with other issues such as SPF, DKIM, or DMARC errors, it can erode trust in the sender domain and indirectly affect email deliverability and reputation.
2. Do I need more than one MX record for better reliability?
Yes. Multiple MX records provide redundancy if the primary mail server goes down; a secondary server ensures emails are still received.
3. What MX setup is recommended for cold email or outreach campaigns?
Use a properly configured domain with valid MX records, hosted by a reputable provider (e.g., Google Workspace, Microsoft 365). Many senders also use a separate domain or subdomain for outreach, but MX accuracy, SPF, DKIM, proper warm-up, and good sending practice matters more.
4. Does an MX record verify whether a specific email user exists?
No. An MX record only shows which mail server receives mail for a domain. It doesn’t confirm whether name@example.com is an active mailbox.
5. What information does an MX record actually provide?
It tells the internet where to deliver emails for a domain and the priority order of mail servers. It does not reveal the existence of the mailbox.
