
Generate a DMARC Record for your domain with the ExactVerify easy-to-use DMARC Record Generator Tool. Create a valid DMARC record in seconds and add it to your DNS to monitor email activity, prevent spoofing, and protect your domain from unauthorized use. Improve email authentication and visibility with a properly configured DMARC policy. Start generating your DMARC record now.
Anti-Spoofing
Email Authentication
Domain Protection
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is a policy that helps prevent email spoofing, phishing, and email threats. It enables domain owners to specify how email from their domain should be managed if it fails authentication checks, such as SPF (Sender Policy Framework) or DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail).
A DMARC record is a DNS TXT record that works with SPF and DKIM to authenticate emails sent from your domain. By publishing a DMARC record, domain owners can prevent unauthorized use of their domain, improve email deliverability, and receive reports on email activity to monitor potential security threats.
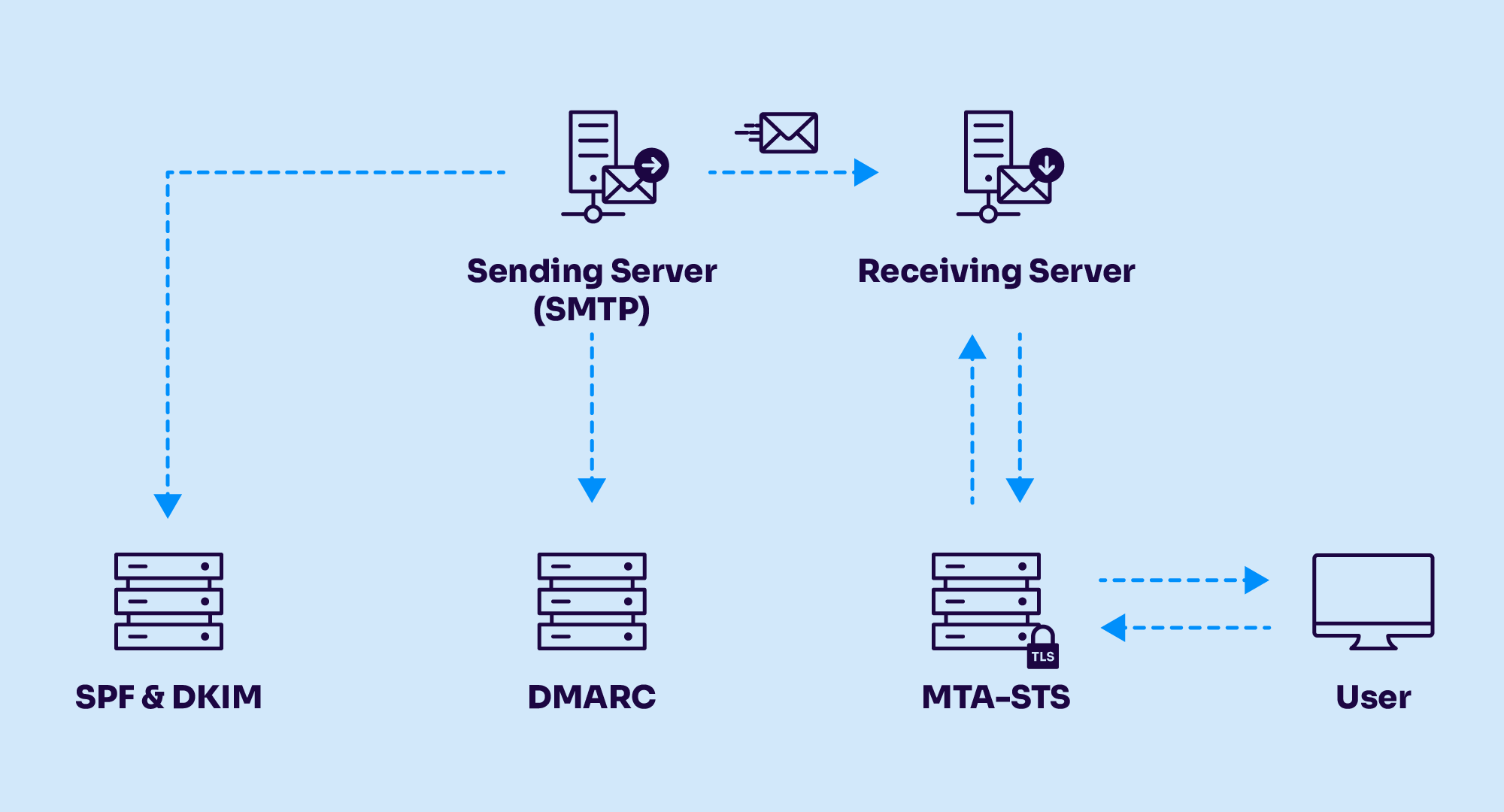
To implement DMARC, an email domain must have SPF (Sender Policy Framework) or DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) configured, along with a published DMARC record in the domain’s DNS. The DMARC record contains authentication rules that recipient mail servers use to determine how to process incoming emails.
The domain owner publishes a DMARC DNS record through their hosting provider, setting the authentication rules and making them visible to mail servers worldwide.

When an email arrives, the recipient’s mail server checks the sender’s domain to see if a DMARC record exists.

The server then verifies the email using SPF and DKIM:
Based on the authentication results, the recipient server follows the DMARC policy: None, Quarantine, or Reject.

Finally, aggregate and forensic reports are sent to the email addresses mentioned in the DMARC record, helping domain owners monitor usage, track email activity, and identify spoofing attempts.

The ExactVerify DMARC Record Generator streamlines this process, enabling you to quickly generate a valid DMARC TXT record in just a few steps, thereby ensuring robust email security and improved deliverability.
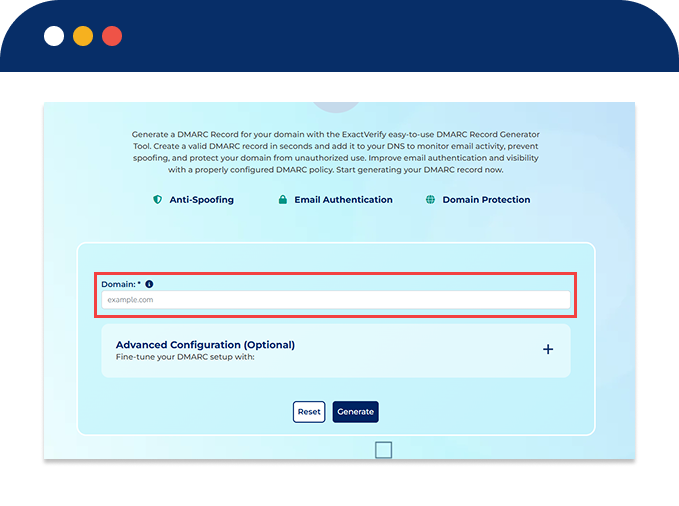
Use the DMARC record generator to create a DMARC Record in simple steps outlined below:
Type in the domain you want to protect (e.g., yourdomain.com).
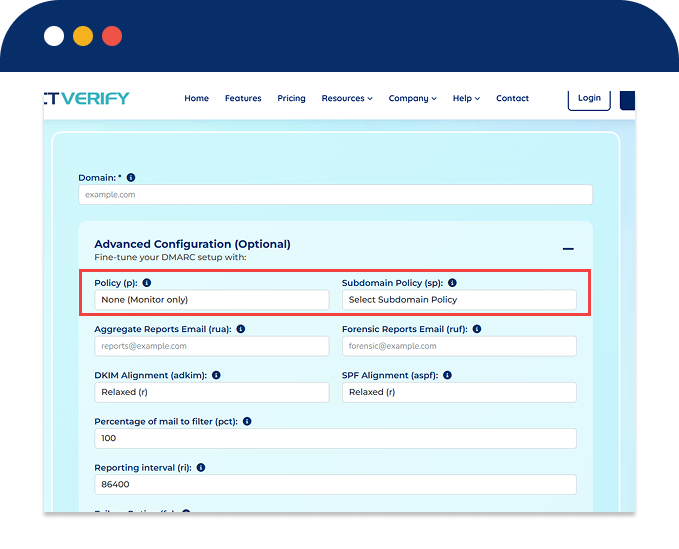
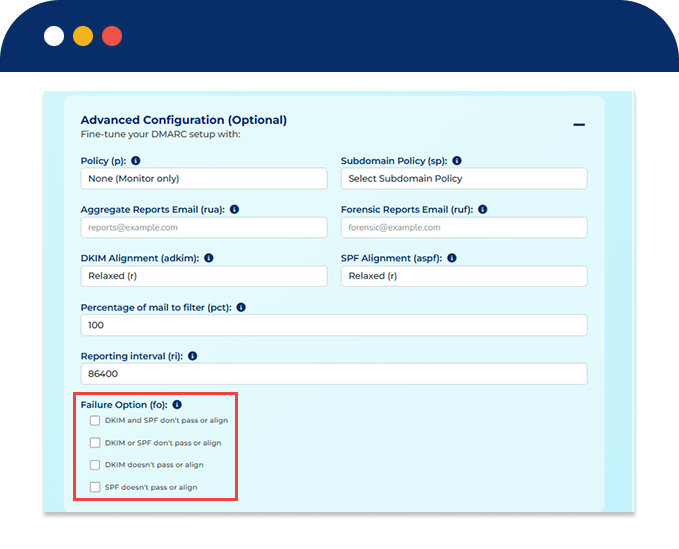
Policy (p): Choose how strict you want email authentication to be:
Subdomain Policy (sp): Control how subdomains (like mail.yourdomain.com) are handled.
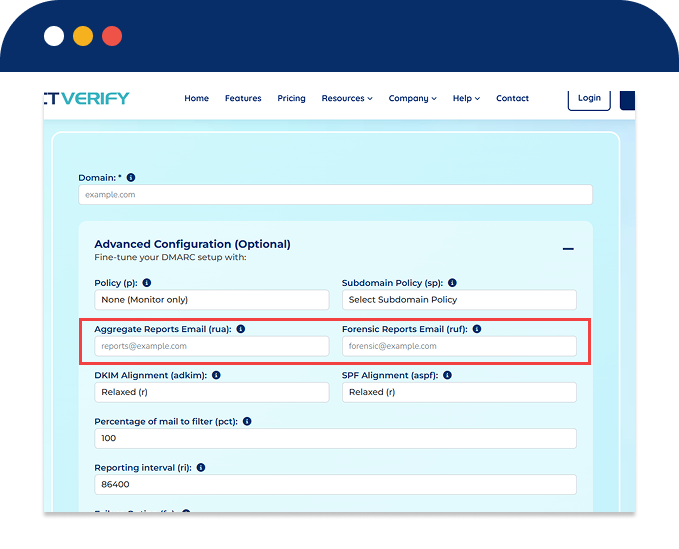
Aggregate Reports (RUA):
Daily reports with SPF, DKIM, and DMARC results.
Forensic Reports (RUF):
Real-time forensic reports when an email fails authentication.
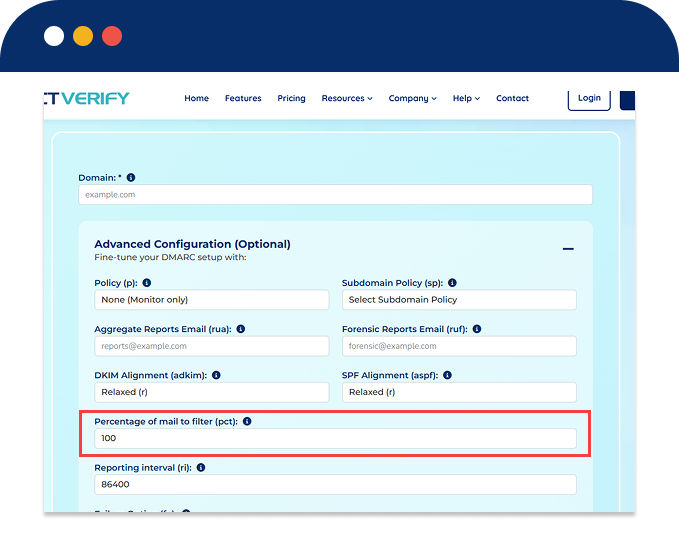
Apply policy to 100% of emails (default) or test with a lower percentage.
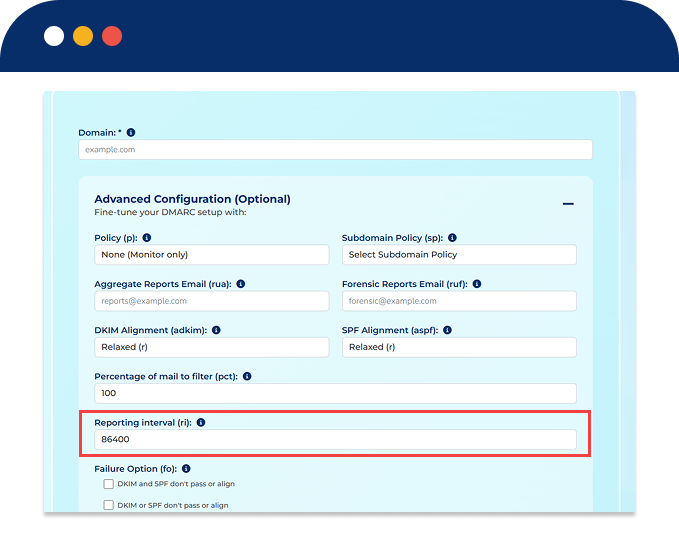
The default interval is 24 hours (86,400 seconds).
Specifies when forensic reports are generated based on SPF or DKIM failures.
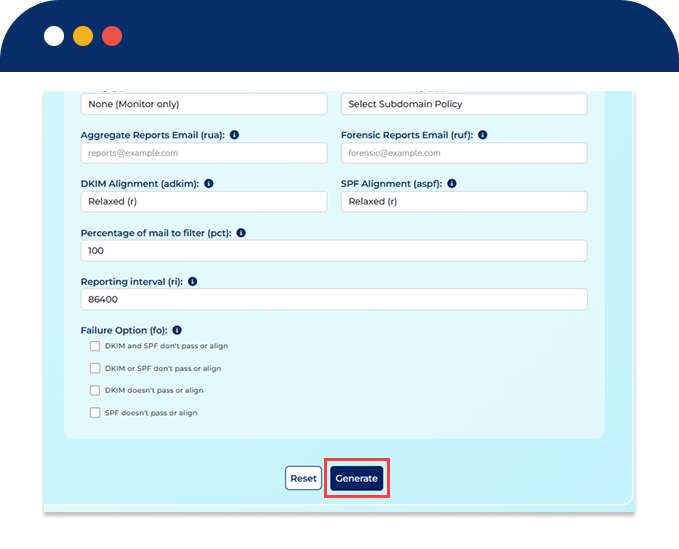
Click Generate to create your DMARC TXT record instantly.
Add the record to your DNS:
Propagation may take 24–48 hours, depending on your DNS provider.
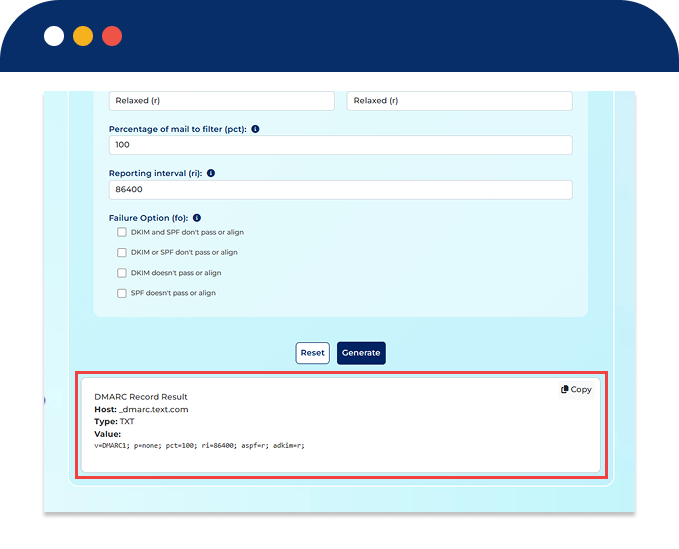
A DMARC record is a plain-text string containing specific tags that define your email authentication policy. The DMARC Record Creator simplifies this by generating this string for you. Below is an overview of the most common DMARC tags:
| Tag | Purpose | Description |
|---|---|---|
| v | Protocol Version Identifier | Must be set to "DMARC1". This tag signals that the record is a valid DMARC policy. |
| p | Domain Policy | Defines the action for emails failing DMARC checks: "none" (monitor only), "quarantine" (send to spam), or "reject" (block delivery). |
| rua | Aggregate Report URI | Specifies the email address to receive daily aggregate reports in XML format, providing overall email traffic statistics. |
| ruf | Failure Report URI | Specifies the email address to receive forensic (failure) reports for individual authentication failures. |
| sp | Subdomain Policy | Sets the DMARC policy specifically for subdomains (e.g., blog.yourdomain.com). |
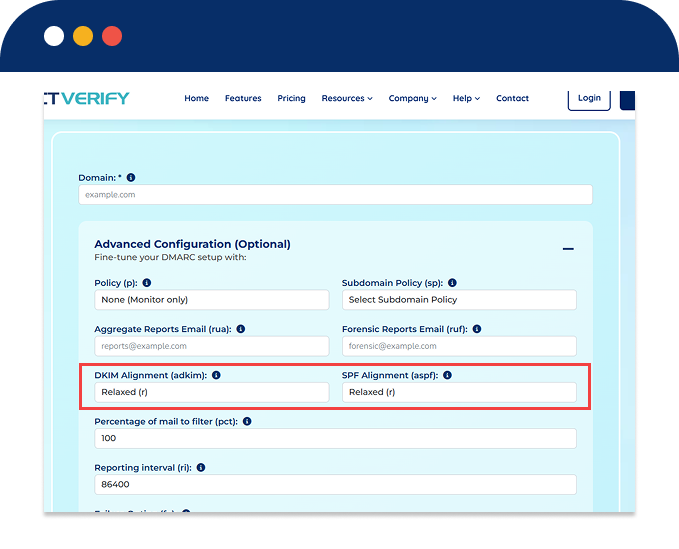
| adkim | DKIM Alignment Mode |
Sets DKIM identifier alignment: "r" (relaxed, default) or "s" (strict). For example, mail.example.com aligns with example.com |
| aspf | SPF Alignment Mode |
Sets SPF identifier alignment: "r" (relaxed, default) or "s" (strict). For example, example.com must match example.com precisely. |
| fo | Failure Reporting Options | Controls conditions triggering forensic reports: e.g., "1" for any failure, "0" for all failures. |
| pct | Policy Application Percentage | Percentage (0–100) of emails the DMARC policy should apply to; useful for phased rollouts. |
| ri | Aggregate Report Interval | Frequency (in seconds) for receiving aggregate reports; default is 86400 (24 hours). |
v=DMARC1; p=none; sp=none; pct=100; rua=mailto:dmarc_reports@yourdomain.com; ruf=mailto:dmarc_reports@yourdomain.com; ri=86400; aspf=r; adkim=r;
